2025
A Deep Dive Into Cross-Dataset Entity Matching with Large and Small Language Models
Zeyu Zhang, Paul Groth, Iacer Calixto, Sebastian Schelter
International Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT) 2025
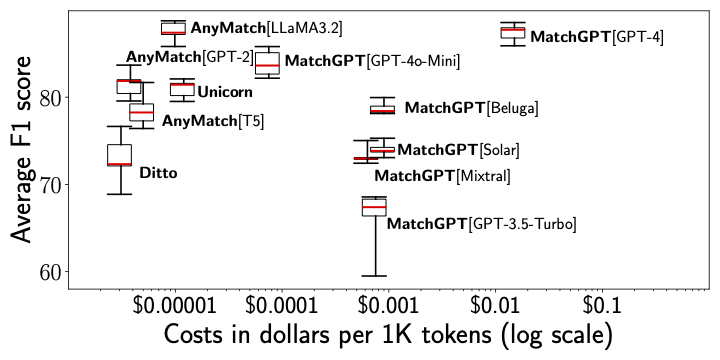
We propose a new challenge that integrates two practical constraints into conventional entity matching (EM) tasks to better align with real-world deployment scenarios. A comprehensive evaluation of eight matching methods across 11 datasets provides key insights into model selection and data profiling.
A Deep Dive Into Cross-Dataset Entity Matching with Large and Small Language Models
Zeyu Zhang, Paul Groth, Iacer Calixto, Sebastian Schelter
International Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT) 2025
We propose a new challenge that integrates two practical constraints into conventional entity matching (EM) tasks to better align with real-world deployment scenarios. A comprehensive evaluation of eight matching methods across 11 datasets provides key insights into model selection and data profiling.
AnyMatch--Efficient Zero-Shot Entity Matching with a Small Language Model
Zeyu Zhang, Paul Groth, Iacer Calixto, Sebastian Schelter
GoodData Workshop, AAAI 2025
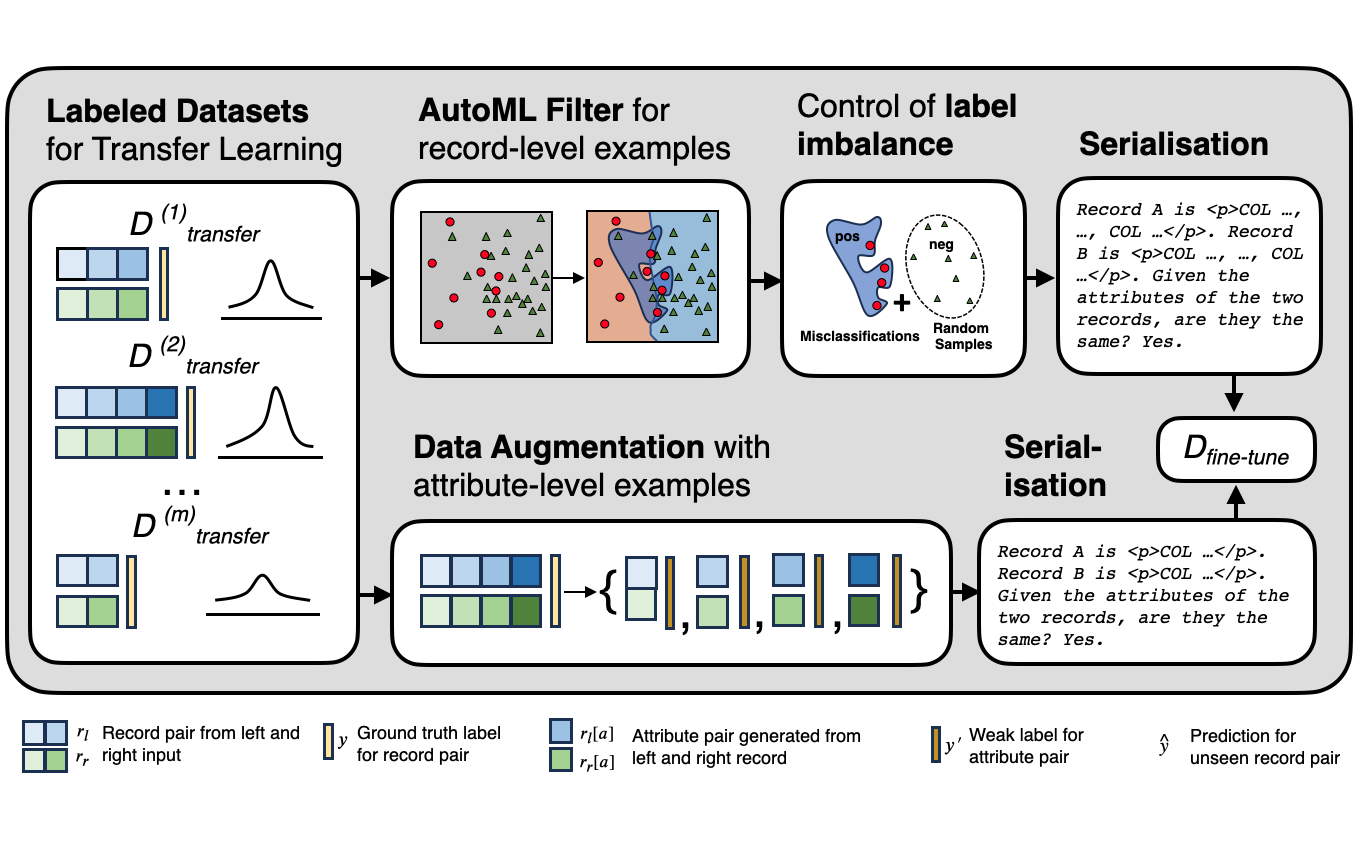
We introduce AnyMatch, a novel framework for building effective and efficient entity matching systems. AnyMatch leverages small language models and borrows idea from instruction tuning to diversify the training corpus, refining the model through multiple data selection strategies. The GPT-2 variant of AnyMatch ranks second among baseline models, achieving an F1 score only 4.4$\%$ lower than GPT-4 in a zero-shot setting, while reducing costs by a factor of 3,899.
AnyMatch--Efficient Zero-Shot Entity Matching with a Small Language Model
Zeyu Zhang, Paul Groth, Iacer Calixto, Sebastian Schelter
GoodData Workshop, AAAI 2025
We introduce AnyMatch, a novel framework for building effective and efficient entity matching systems. AnyMatch leverages small language models and borrows idea from instruction tuning to diversify the training corpus, refining the model through multiple data selection strategies. The GPT-2 variant of AnyMatch ranks second among baseline models, achieving an F1 score only 4.4$\%$ lower than GPT-4 in a zero-shot setting, while reducing costs by a factor of 3,899.
2024
Directions Towards Efficient and Automated Data Wrangling with Large Language Models
Zeyu Zhang, Paul Groth, Iacer Calixto, Sebastian Schelter
IEEE 40th International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops (ICDEW) 2024
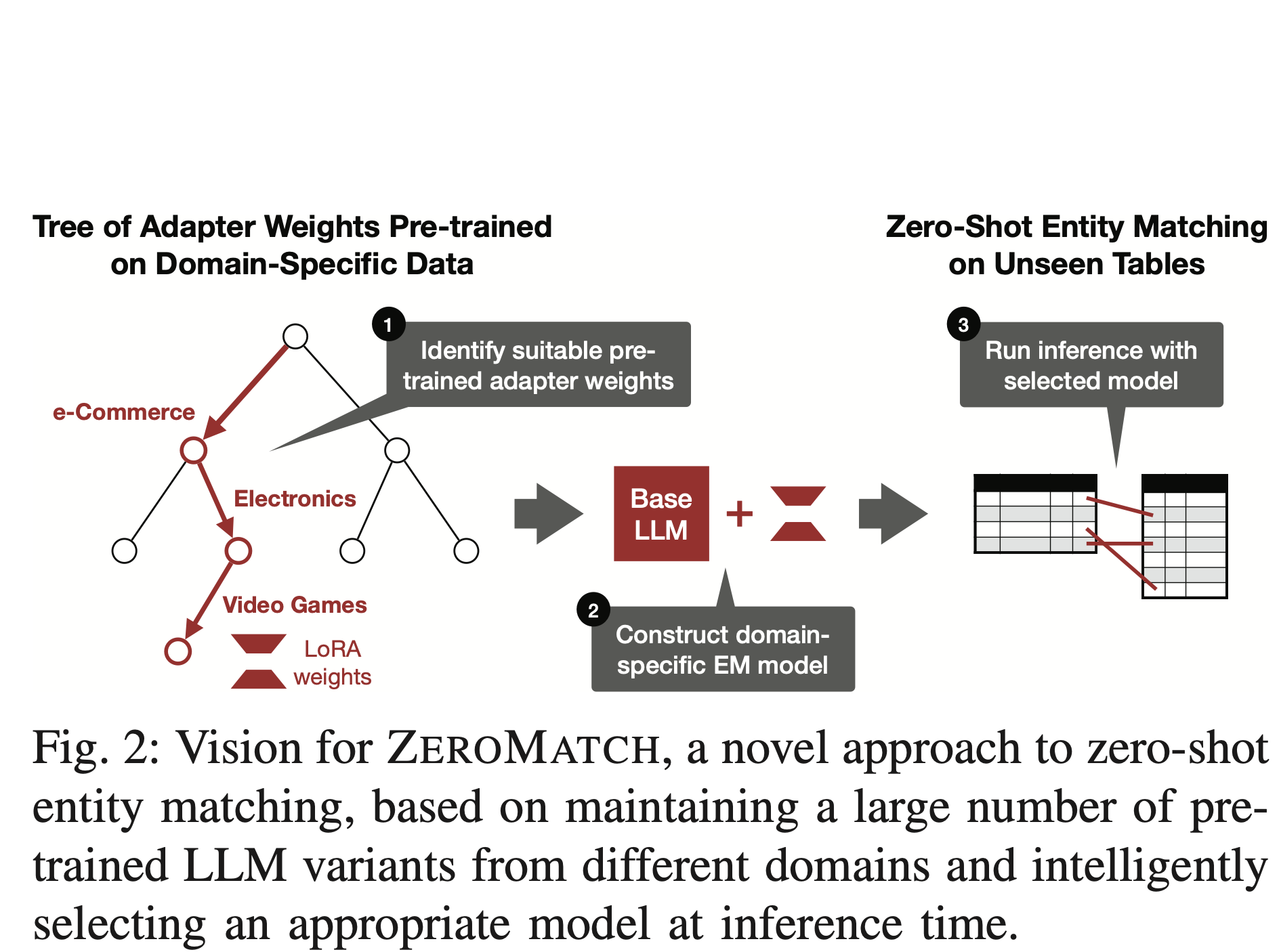
Parameter-efficient tuning (PEFT) methods hold great promise for developing lightweight data wrangling applications. In this study, we evaluate the effectiveness of four popular PEFT methods across three real-world data wrangling tasks, providing insights to guide future research.
Directions Towards Efficient and Automated Data Wrangling with Large Language Models
Zeyu Zhang, Paul Groth, Iacer Calixto, Sebastian Schelter
IEEE 40th International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops (ICDEW) 2024
Parameter-efficient tuning (PEFT) methods hold great promise for developing lightweight data wrangling applications. In this study, we evaluate the effectiveness of four popular PEFT methods across three real-world data wrangling tasks, providing insights to guide future research.
Red Onions, Soft Cheese and Data: From Food Safety to Data Traceability for Responsible AI.
Stefan Grafberger, Zeyu Zhang, Sebastian Schelter, Ce Zhang
IEEE Data Eng. Bull. 2024
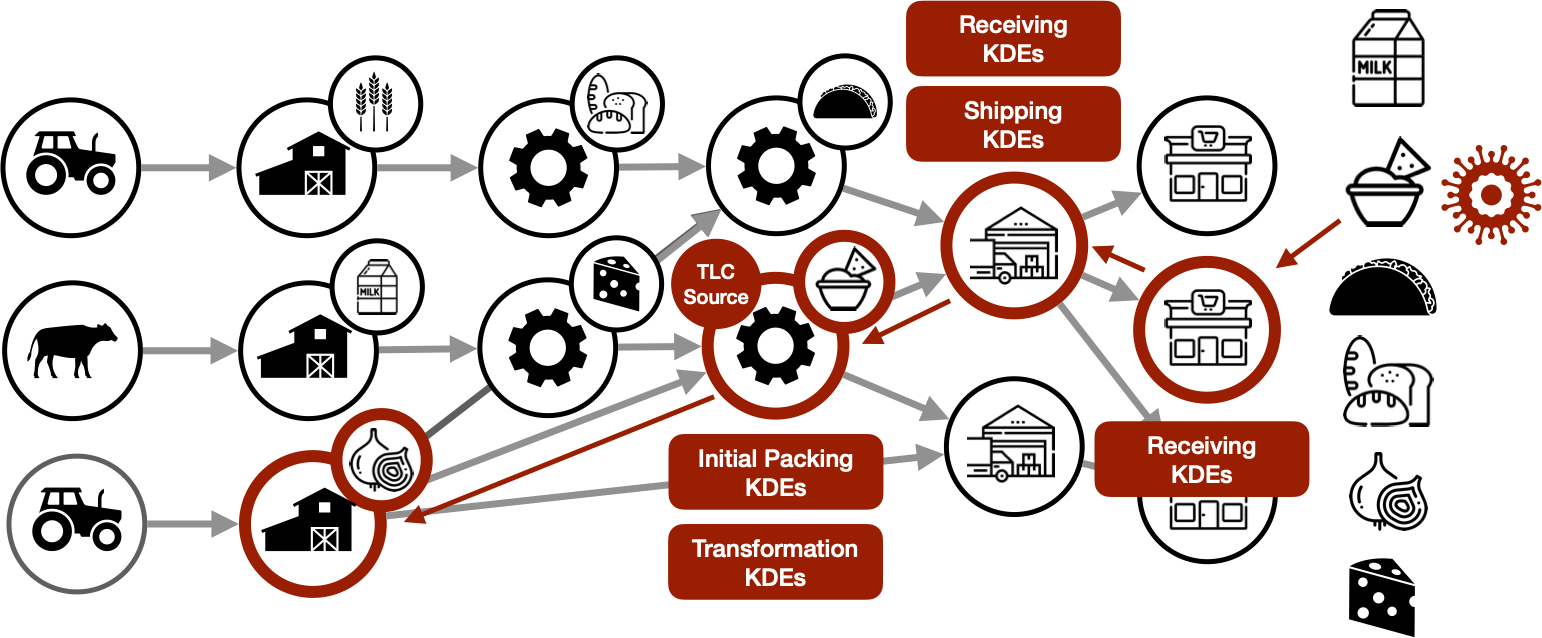
Software systems that learn from data with AI and machine learning (ML) are becoming ubiquitous and are increasingly used to automate impactful decisions. The risks arising from this widespread use of AI/ML are garnering attention from policy makers, scientists, and the media, and lead to the question what data management research can contribute to reduce such risks. These dangers of AI/ML applications are relatively new and recent, however our societies have had to deal with the dangers of complex and distributed technical processes for a long time already. Based on this insight, we detail how the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) combats the outbreaks of foodborne illnesses, and use their processes as an inspiration for a data-centric vision towards responsible AI.
Red Onions, Soft Cheese and Data: From Food Safety to Data Traceability for Responsible AI.
Stefan Grafberger, Zeyu Zhang, Sebastian Schelter, Ce Zhang
IEEE Data Eng. Bull. 2024
Software systems that learn from data with AI and machine learning (ML) are becoming ubiquitous and are increasingly used to automate impactful decisions. The risks arising from this widespread use of AI/ML are garnering attention from policy makers, scientists, and the media, and lead to the question what data management research can contribute to reduce such risks. These dangers of AI/ML applications are relatively new and recent, however our societies have had to deal with the dangers of complex and distributed technical processes for a long time already. Based on this insight, we detail how the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) combats the outbreaks of foodborne illnesses, and use their processes as an inspiration for a data-centric vision towards responsible AI.
2021
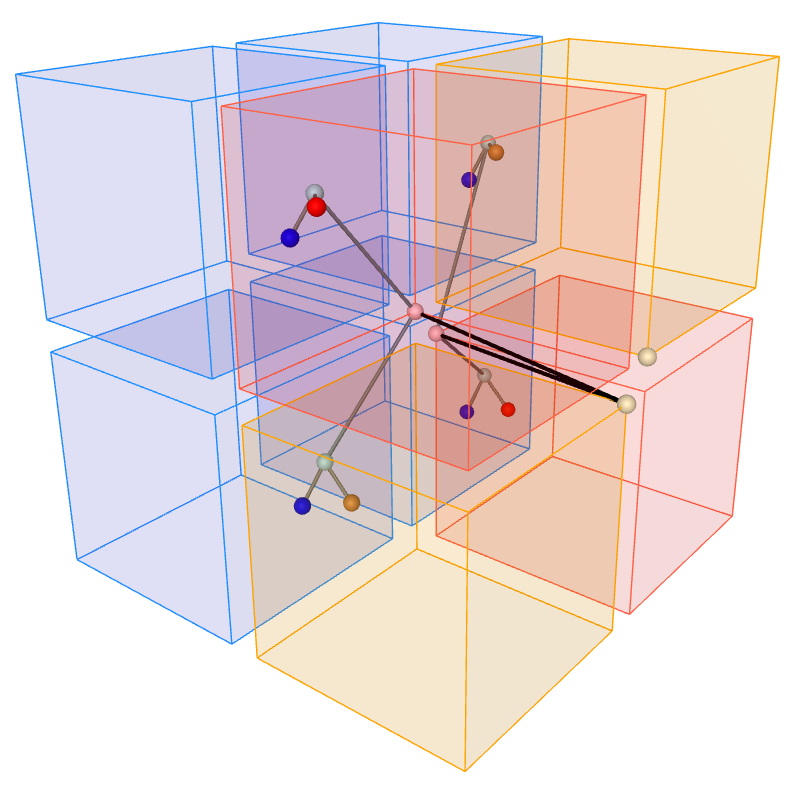
Compact 3D Grid Drawings of Trees
Irene Parada, Kees Voorintholt, Zeyu Zhang
Graph Drawing and Network Visualization: 29th International Symposium 2021
We show that perfect binary trees with $n-1$ vertices can be optimally embedded in 3D, that is, they admit a straight-line drawing on a $\sqrt[3]{n}$ by $\sqrt[3]{n}$ by $\sqrt[3]{n}$ grid without intersecting edges. To show it, we adapt a recursive approach used in 2D by Akitaya~\etal~[GD'18] to construct compact embeddings of perfect binary trees on a square grid.
Compact 3D Grid Drawings of Trees
Irene Parada, Kees Voorintholt, Zeyu Zhang
Graph Drawing and Network Visualization: 29th International Symposium 2021
We show that perfect binary trees with $n-1$ vertices can be optimally embedded in 3D, that is, they admit a straight-line drawing on a $\sqrt[3]{n}$ by $\sqrt[3]{n}$ by $\sqrt[3]{n}$ grid without intersecting edges. To show it, we adapt a recursive approach used in 2D by Akitaya~\etal~[GD'18] to construct compact embeddings of perfect binary trees on a square grid.
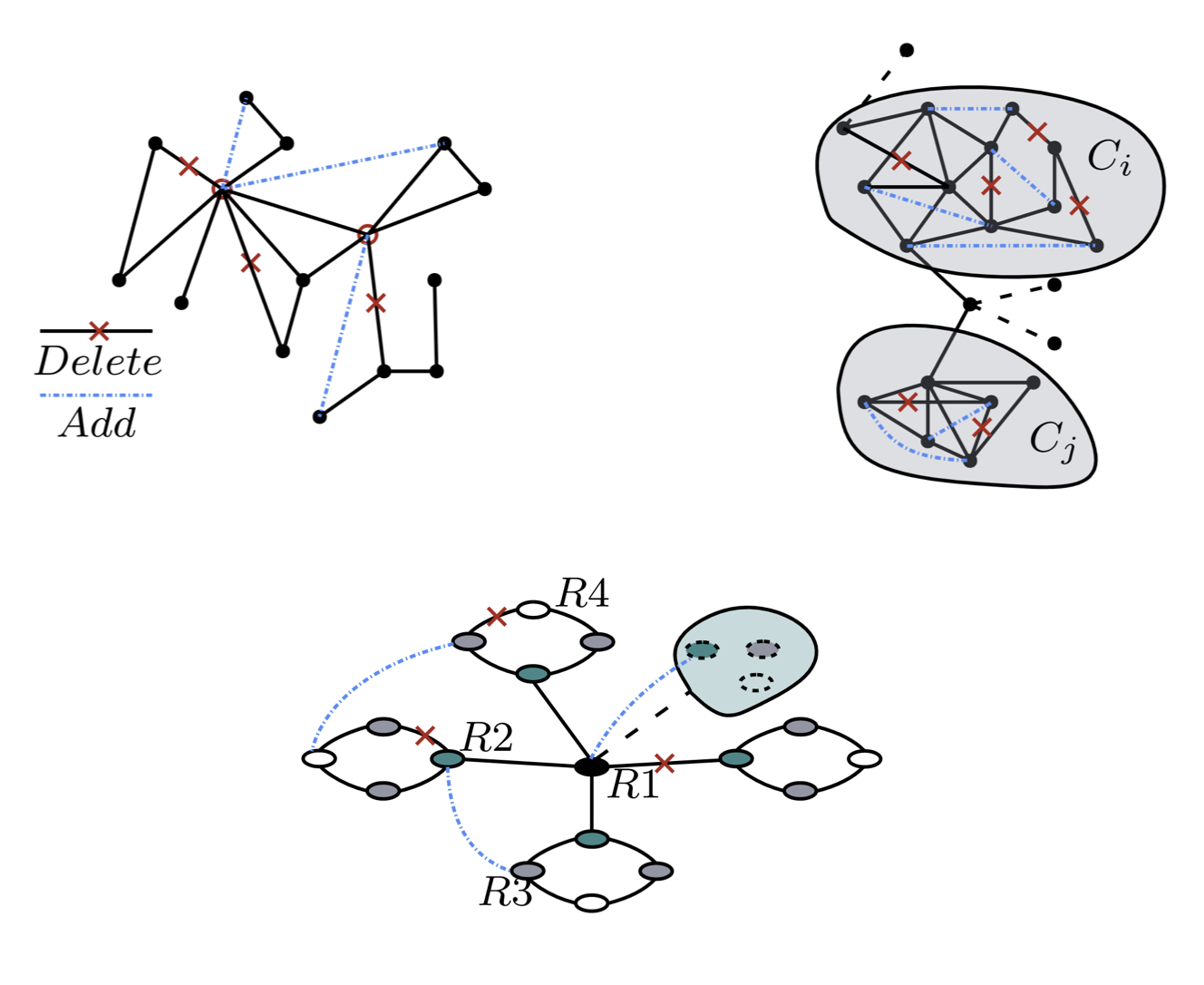
A comparative study on robust graph neural networks to structural noises
Zeyu Zhang, Yulong Pei
DLG Workshop, AAAI 2021
We introduce three levels of structural noise—local, community, and global—and systematically compare existing robust GNNs under these consistent noise settings. From a model perspective, we categorize the robust GNNs into sample-based, revision-based, and construction-based approaches. Based on empirical results, we offer practical recommendations for the design of more robust GNNs.
A comparative study on robust graph neural networks to structural noises
Zeyu Zhang, Yulong Pei
DLG Workshop, AAAI 2021
We introduce three levels of structural noise—local, community, and global—and systematically compare existing robust GNNs under these consistent noise settings. From a model perspective, we categorize the robust GNNs into sample-based, revision-based, and construction-based approaches. Based on empirical results, we offer practical recommendations for the design of more robust GNNs.